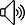使用狄克斯特拉算法找出下图中从起点至终点耗时最短的路径,路径上的每个数字表示的都是时间,单位分钟。
狄克斯特拉算法包含的4个步骤:
(1)找出开销/消耗“最便宜”的节点,即在最短时间内到达的节点
(2)对于该节点的邻居,检查是否有前往它们的更短路径,如果有,更新该节点的邻居的开销
(3)重复上述过程,直到对图中的每个节点都这样做了
(4)计算最终路径
python代码实现:
# 描述各节点、时间开销、父节点信息
# 创建节点信息,start起点,fin终点
graph = {}
graph["start"]={}
graph["start"]["a"]=6
graph["start"]["b"]=2
graph["a"] = {}
graph["a"]["fin"]=1
graph["b"] = {}
graph["b"]["a"] = 3
graph["b"]["fin"]=5
graph["fin"]={}
# 创建开销/时间表
infinity = float("inf") #无穷大
costs={}
costs["a"]=6
costs["b"]=2
costs["fin"]=infinity #暂时将通往终点的时间,定义为无穷大
# 路径中父节点信息
parents= {}
parents["a"]="start"
parents["b"]="start"
parents["fin"]=None
# 记录处理过的节点的数组
processed = []
# 定义寻找最小节点的函数
def find_lowest_cost_node(costs):
lowest_cost = float("inf")
lowest_cost_node = None
for node in costs: # 遍历所有节点
cost = costs[node]
if cost < lowest_cost and node not in processed: # 如果当前节点的开销更低且未处理过
lowest_cost = cost
lowest_cost_node = node
return lowest_cost_node
# 寻找最短路径
def find_shortest_path():
node = "fin"
shortest_path = ["fin"]
while parents[node] != "start":
shortest_path.append(parents[node])
node = parents[node]
shortest_path.append("start")
shortest_path.reverse() # 将从终点到起点的路径反序表示
return shortest_path
# 狄克斯特拉算法寻找最短路径
def dijkstra():
node = find_lowest_cost_node(costs) #在未处理的节点中找到开销最小的节点
while node is not None: # 所有节点都被处理过,node为None,循环结束
cost = costs[node]
neighbors = graph[node]
for n in neighbors.keys(): # 遍历当前节点的所有邻居
new_cost = cost + neighbors[n]
if costs[n] > new_cost: # 如果经当前节点前往该邻居更近
costs[n] = new_cost # 就更新该邻居的开销
parents[n] = node # 同时将该邻居的父节点设置为当前节点
processed.append(node) # 将当前节点标记为处理过
node = find_lowest_cost_node(costs) # 找出接下来要处理的节点,并循环
shortest_path = find_shortest_path()
print(shortest_path)
# 运行
dijkstra()
运行结果为:
['start', 'b', 'a', 'fin']
运行后,内部各变量的对应信息如下:
costs = {'a': 5, 'b': 2, 'fin': 6}
graph = {'start': {'a': 6, 'b': 2}, 'a': {'fin': 1}, 'b': {'a': 3, 'fin': 5}, 'fin': {}}
parents = {'a': 'b', 'b': 'start', 'fin': 'a'}
precessed = ['b', 'a', 'fin']
辅助说明:
(1)广度优先搜索用于在非加权图中查找最短路径
(2)狄克斯特拉算法用于在加权图中查找最短路径
(3)仅在权重为正时狄克斯特拉算法才管用
(4)如果图中包含了负权边(节点间开销为负值),请使用贝尔曼-福德算法。